- 1. Basics
- How to Compare Arrays in PostgreSQL
- How to Concatenate Strings in PostgreSQL
- How to Convert the Case of a String
- How to Create an Array
- How to Insert Array Data Into a Table
- How to Insert Data Into an Array
- How to Modify Arrays
- How to Query Arrays
- How to Replace Substrings
- How to Trim Strings
- How to Use string_agg()
- How to Use substring()
- How to Use substring() with Regular Expressions
- How to Insert
- How to Update
- How to Delete
- 2. Database Management
- How to Create a Table
- How to Drop a Table
- How to Rename a Table
- How to Truncate a Table
- How to Duplicate a Table
- How to Add a Column
- How to Drop a Column
- How to Rename a Column
- How to Add a Default Value to a Column
- How to Remove a Default Value From a Column
- How to Add a Not Null Constraint
- How to Remove a Not Null Constraint
- How to Create an Index
- How to Drop an Index
- How to Create a View
- How to Drop a View
- How to Alter Sequence
- 3. Dates And Time
- How to Exclude Current or Partial Weeks
- How to Use BETWEEN Correctly
- How to Query Date and Time
- How to Group by Time
- How to Round Timestamps
- How to Convert Local Time to UTC
- 4. Analysis
- How to Use Lateral Joins
- How to Use nullif()
- How to Get the First Row per Group
- How to Use generate_series to Avoid Gaps In Data
- How to Do Type Casting
- How to Write a Common Table Expression
- How to Import a CSV
- How to Compare Two Values When One Is Null
- How to Use Coalesce
- How to Write a Case Statement
- How to Query a JSON Column
- How to Use Filter Clause to Have Multiple Counts
- How to Calculate Cumulative Sum-Running Total
- 1. Basics
- How to Concatenate Strings in MS-SQL Server
- How to Convert the Case of a String
- How to replace a Substring in a String
- How to Trim Strings
- How to Use string_agg()
- How to Use substring()
- How to Insert
- How to Update
- How to Delete
- 2. Database Management
- How to Create a Table in MS-SQL
- How to Drop a Table in MS-SQL
- How to Rename a Table in MS-SQL
- How to Truncate a Table in MS-SQL
- How to Duplicate a Table in MS-SQL
- How to Add a Column in MS-SQL
- How to Drop a Column in MS-SQL
- How to Rename a Column in MS-SQL
- How to Add a Default Value to a Column in MS-SQL
- How to Remove a Default Value From a Column in MS-SQL
- How to Add a Not Null Constraint in MS-SQL
- How to Remove a Not Null Constraint in MS-SQL
- How to Create an Index in MS-SQL
- How to Drop an Index in MS-SQL
- How to Create a View in MS-SQL
- How to Drop a View in MS-SQL
- How to Alter Sequence in MS-SQL
- 3. Dates And Time
- How to Exclude Current or Partial Weeks
- How to Use BETWEEN Correctly
- How to Query Date and Time in MS-SQL
- How to Group by Time
- How to Extract a Component From a Datetime
- 4. Analysis
- How to Use Lateral Joins
- How to Use nullif()
- How to Get the First Row per Group
- How to Do Type Casting in MS-SQL
- How to Write a Common Table Expression
- How to Import a CSV
- How to Use Coalesce
- How to Write a Case Statement
- How to Query a JSON Column
- How to Calculate Cumulative Sum-Running Total
- 1. Basics
- How to Concatenate Strings in MySQL
- How to Convert the Case of a String
- How to replace a Substring in a String
- How to Trim a String
- How to use group_concat()
- How to do you Use a substring()
- How to Use substring() with Regular Expressions
- How to use insert into statement
- How to use Update statement in SQL
- How to use Delete SQL Statement
- 2. Database Management
- How to Create a Table in MySQL
- How to Drop a Table in MySQL
- How to Rename a Table in MySQL
- How to Truncate a Table in MySQL
- How to Duplicate a Table in MySQL
- How to Add a Column in MySQL
- How to Drop a Column in MySQL
- How to Rename a Column in MySQL
- How to Add a Default Value to a Column in MySQL
- How to Remove a Default Value From a Column in MySQL
- How to Add a Not Null Constraint in MySQL
- How to Remove a Not Null Constraint in MySQL
- How to Create an Index in MySQL
- How to Drop an Index in MySQL
- How to Create a View in MySQL
- How to Drop a View in MySQL
- How to Alter Sequence in MySQL
- 3. Dates And Time
- How to Exclude Current or Partial Weeks
- How to Use BETWEEN Correctly
- How to Query Date and Time in MySQL
- How to Group by Time
- How to Round Timestamps
- 4. Analysis
- How to Use nullif()
- How to Get the First Row per Group
- How to Do Type Casting in MySQL
- How to Write a Common Table Expression
- How to Import a CSV
- How to Use Coalesce
- How to Write a Case Statement
- How to Query a JSON Column
- How to Calculate Cumulative Sum-Running Total
- 1. Basics
- How to Concatenate Strings in Oracle
- How to Convert the Case of a String
- How to Replace Substrings
- How to Trim Strings
- How to Use listagg()
- How to Use substring()
- How to Use substring() with Regular Expressions
- How to Insert
- How to Update
- How to Delete
- 2. Database Management
- How to Create a Table
- How to Drop a Table
- How to Rename a Table
- How to Truncate a Table
- How to Duplicate a Table
- How to Add a Column
- How to Drop a Column
- How to Rename a Column
- How to Add a Default Value to a Column
- How to Remove a Default Value From a Column
- How to Add a Not Null Constraint
- How to Remove a Not Null Constraint
- How to Create an Index
- How to Drop an Index
- How to Create a View
- How to Drop a View
- How to Alter Sequence
- 3. Dates And Time
- How to Exclude Current or Partial Weeks
- How to Use BETWEEN Correctly
- How to Query Date and Time
- How to Group by Time
- How to Round Timestamps
- 4. Analysis
- How to Use nullif()
- How to Get the First Row per Group
- How to Do Type Casting
- How to Write a Common Table Expression
- How to Import a CSV
- How to Use Coalesce
- How to Write a Case Statement
- How to Query a JSON Column
- How to Use Filter Clause to Have Multiple Counts
- How to Calculate Cumulative Sum-Running Total
- 1. Basics
- How to Concatenate Strings in BigQuery
- How to Convert the Case of a String
- How to replace a Substring in a String
- How to Trim a String
- How to Use string_agg()
- How to use substring() function
- How to Use substring() with Regular Expressions
- How to Use BETWEEN Correctly
- How to use insert into statement
- How to use Update statement in SQL
- How to use Delete SQL Statement
- 2. Database Management
- How to Create a Database in BigQuery
- How to Create a Table in BigQuery
- How to Drop a Table in BigQuery
- How to Rename a Table in BigQuery
- How to Truncate Table in BigQuery
- How to Duplicate a Table in BigQuery
- How to Add a Column in BigQuery
- How to Drop a Column in BigQuery
- How to Add a Default Value to a Column in BigQuery
- How to Add a Not Null Constraint in BigQuery
- How to Remove a Not Null Constraint in BigQuery
- How to Create a View in BigQuery
- How to Drop a View in BigQuery
- 3. Dates And Time
- How to Exclude Current or Partial Weeks
- How to Query Date and Time
- How to Group by Time
- How to Round Timestamps
- 4. Analysis
- How to Use nullif()
- How to Get the First Row per Group
- How to Do Type Casting
- How to Write a Common Table Expression
- How to Compare Two Values When One Is Null
- How to Use Coalesce
- How to Write a Case Statement
- How to Calculate Cumulative Sum-Running Total
SQL Indexes
- 1. Basics
- How to Compare Arrays in PostgreSQL
- How to Concatenate Strings in PostgreSQL
- How to Convert the Case of a String
- How to Create an Array
- How to Insert Array Data Into a Table
- How to Insert Data Into an Array
- How to Modify Arrays
- How to Query Arrays
- How to Replace Substrings
- How to Trim Strings
- How to Use string_agg()
- How to Use substring()
- How to Use substring() with Regular Expressions
- How to Insert
- How to Update
- How to Delete
- 2. Database Management
- How to Create a Table
- How to Drop a Table
- How to Rename a Table
- How to Truncate a Table
- How to Duplicate a Table
- How to Add a Column
- How to Drop a Column
- How to Rename a Column
- How to Add a Default Value to a Column
- How to Remove a Default Value From a Column
- How to Add a Not Null Constraint
- How to Remove a Not Null Constraint
- How to Create an Index
- How to Drop an Index
- How to Create a View
- How to Drop a View
- How to Alter Sequence
- 3. Dates And Time
- How to Exclude Current or Partial Weeks
- How to Use BETWEEN Correctly
- How to Query Date and Time
- How to Group by Time
- How to Round Timestamps
- How to Convert Local Time to UTC
- 4. Analysis
- How to Use Lateral Joins
- How to Use nullif()
- How to Get the First Row per Group
- How to Use generate_series to Avoid Gaps In Data
- How to Do Type Casting
- How to Write a Common Table Expression
- How to Import a CSV
- How to Compare Two Values When One Is Null
- How to Use Coalesce
- How to Write a Case Statement
- How to Query a JSON Column
- How to Use Filter Clause to Have Multiple Counts
- How to Calculate Cumulative Sum-Running Total
- 1. Basics
- How to Concatenate Strings in MS-SQL Server
- How to Convert the Case of a String
- How to replace a Substring in a String
- How to Trim Strings
- How to Use string_agg()
- How to Use substring()
- How to Insert
- How to Update
- How to Delete
- 2. Database Management
- How to Create a Table in MS-SQL
- How to Drop a Table in MS-SQL
- How to Rename a Table in MS-SQL
- How to Truncate a Table in MS-SQL
- How to Duplicate a Table in MS-SQL
- How to Add a Column in MS-SQL
- How to Drop a Column in MS-SQL
- How to Rename a Column in MS-SQL
- How to Add a Default Value to a Column in MS-SQL
- How to Remove a Default Value From a Column in MS-SQL
- How to Add a Not Null Constraint in MS-SQL
- How to Remove a Not Null Constraint in MS-SQL
- How to Create an Index in MS-SQL
- How to Drop an Index in MS-SQL
- How to Create a View in MS-SQL
- How to Drop a View in MS-SQL
- How to Alter Sequence in MS-SQL
- 3. Dates And Time
- How to Exclude Current or Partial Weeks
- How to Use BETWEEN Correctly
- How to Query Date and Time in MS-SQL
- How to Group by Time
- How to Extract a Component From a Datetime
- 4. Analysis
- How to Use Lateral Joins
- How to Use nullif()
- How to Get the First Row per Group
- How to Do Type Casting in MS-SQL
- How to Write a Common Table Expression
- How to Import a CSV
- How to Use Coalesce
- How to Write a Case Statement
- How to Query a JSON Column
- How to Calculate Cumulative Sum-Running Total
- 1. Basics
- How to Concatenate Strings in MySQL
- How to Convert the Case of a String
- How to replace a Substring in a String
- How to Trim a String
- How to use group_concat()
- How to do you Use a substring()
- How to Use substring() with Regular Expressions
- How to use insert into statement
- How to use Update statement in SQL
- How to use Delete SQL Statement
- 2. Database Management
- How to Create a Table in MySQL
- How to Drop a Table in MySQL
- How to Rename a Table in MySQL
- How to Truncate a Table in MySQL
- How to Duplicate a Table in MySQL
- How to Add a Column in MySQL
- How to Drop a Column in MySQL
- How to Rename a Column in MySQL
- How to Add a Default Value to a Column in MySQL
- How to Remove a Default Value From a Column in MySQL
- How to Add a Not Null Constraint in MySQL
- How to Remove a Not Null Constraint in MySQL
- How to Create an Index in MySQL
- How to Drop an Index in MySQL
- How to Create a View in MySQL
- How to Drop a View in MySQL
- How to Alter Sequence in MySQL
- 3. Dates And Time
- How to Exclude Current or Partial Weeks
- How to Use BETWEEN Correctly
- How to Query Date and Time in MySQL
- How to Group by Time
- How to Round Timestamps
- 4. Analysis
- How to Use nullif()
- How to Get the First Row per Group
- How to Do Type Casting in MySQL
- How to Write a Common Table Expression
- How to Import a CSV
- How to Use Coalesce
- How to Write a Case Statement
- How to Query a JSON Column
- How to Calculate Cumulative Sum-Running Total
- 1. Basics
- How to Concatenate Strings in Oracle
- How to Convert the Case of a String
- How to Replace Substrings
- How to Trim Strings
- How to Use listagg()
- How to Use substring()
- How to Use substring() with Regular Expressions
- How to Insert
- How to Update
- How to Delete
- 2. Database Management
- How to Create a Table
- How to Drop a Table
- How to Rename a Table
- How to Truncate a Table
- How to Duplicate a Table
- How to Add a Column
- How to Drop a Column
- How to Rename a Column
- How to Add a Default Value to a Column
- How to Remove a Default Value From a Column
- How to Add a Not Null Constraint
- How to Remove a Not Null Constraint
- How to Create an Index
- How to Drop an Index
- How to Create a View
- How to Drop a View
- How to Alter Sequence
- 3. Dates And Time
- How to Exclude Current or Partial Weeks
- How to Use BETWEEN Correctly
- How to Query Date and Time
- How to Group by Time
- How to Round Timestamps
- 4. Analysis
- How to Use nullif()
- How to Get the First Row per Group
- How to Do Type Casting
- How to Write a Common Table Expression
- How to Import a CSV
- How to Use Coalesce
- How to Write a Case Statement
- How to Query a JSON Column
- How to Use Filter Clause to Have Multiple Counts
- How to Calculate Cumulative Sum-Running Total
- 1. Basics
- How to Concatenate Strings in BigQuery
- How to Convert the Case of a String
- How to replace a Substring in a String
- How to Trim a String
- How to Use string_agg()
- How to use substring() function
- How to Use substring() with Regular Expressions
- How to Use BETWEEN Correctly
- How to use insert into statement
- How to use Update statement in SQL
- How to use Delete SQL Statement
- 2. Database Management
- How to Create a Database in BigQuery
- How to Create a Table in BigQuery
- How to Drop a Table in BigQuery
- How to Rename a Table in BigQuery
- How to Truncate Table in BigQuery
- How to Duplicate a Table in BigQuery
- How to Add a Column in BigQuery
- How to Drop a Column in BigQuery
- How to Add a Default Value to a Column in BigQuery
- How to Add a Not Null Constraint in BigQuery
- How to Remove a Not Null Constraint in BigQuery
- How to Create a View in BigQuery
- How to Drop a View in BigQuery
- 3. Dates And Time
- How to Exclude Current or Partial Weeks
- How to Query Date and Time
- How to Group by Time
- How to Round Timestamps
- 4. Analysis
- How to Use nullif()
- How to Get the First Row per Group
- How to Do Type Casting
- How to Write a Common Table Expression
- How to Compare Two Values When One Is Null
- How to Use Coalesce
- How to Write a Case Statement
- How to Calculate Cumulative Sum-Running Total
An SQL index is an independently stored data structure that belongs to a table. A table can have zero or more indexes. When used appropriately, an SQL index can speed up your query. SQL indexes are primarily used with WHERE, JOIN or ORDER BY clauses to optimize the access of few records. Indexes are not typically used in analytical environments where queries access big portions of the involved tables.
In these examples, there is an index on table population with a key on the last_name column. This query uses the index:
SELECT ssn, last_name
FROM population
WHERE last_name = ‘Smith1234567’
This query cannot use the index as the WHERE clause is using the first_name column:
SELECT ssn, last_name
FROM population
WHERE first_name = ‘John1234567’
Cost of SQL Indexes
Since indexes are data structures associated with a table, all changes to the table must be also applied to the index. Inserts, deletes, and updates to tables with indexes are slower as they perform more write operations.
Before creating an index, evaluate the cost benefit relationship. You should only create an index where the benefit exceeds the cost. To identify the indexes that have the best benefit:
- Identify frequently executed queries with slow response times.
- Identify which queries can be accelerated using an index.
- Evaluate cost-benefit ratio of the proposed index.
Verify Indexes are being Used
If you have a slow query with an index, verify the index is actually being used. Once technique is the EXPLAIN statement. Review Show Me the Best Execution Plan in the Query Optimization tutorial.
Here is the query:
SELECT ssn, last_name
FROM population
WHERE lower ( last_name ) = ‘smith 10000002’
Run the query with the EXPLAIN execution plan:
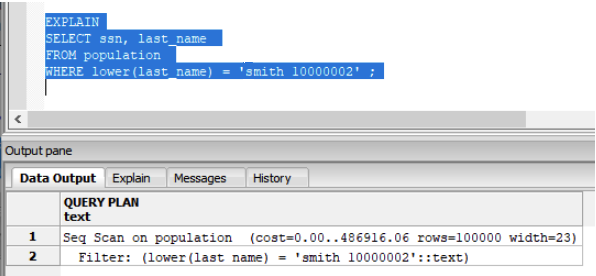
In the EXPLAIN output you see it ran a Sequential Scan instead of the expected Index Scan on the last_name column. What happened? The problem is the lower() function. You cannot have a function or operation on a column if you want to use it as an index.
Refactor your query:
SELECT ssn, last_name
FROM population
WHERE last_name = ‘smith 10000002’
Run the EXPLAIN execution plan on the refactored query:
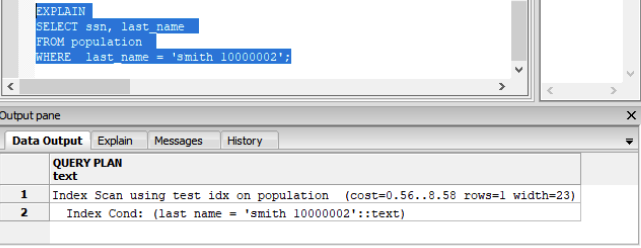
The expected Index scan is used.
SQL Indexes Based on Expressions
As you learned, if you use a function or operation in the WHERE clause on the index key column, the index is not used in the query. Instead, a sequential scan is run.
To solve this limitation, some databases offer a special Functional index to support an expression as the index key.
In the PostgreSQL dialect you can use CREATE INDEX to create a functional index using the expression lower(last_name):
CREATE INDEX functional_index
ON population ( lower(last_name) )
Run the EXPLAIN execution plan on the query:
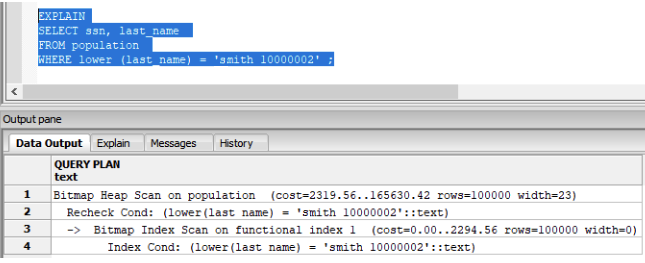
Success! The query execution plan is using an index scan.
Query Refactorization
In SQL, there are many ways to write a query to return the same results. You can refactor a slow query to use different clauses or conditions while returning the same results.
Here are some refactor techniques to try and improve query performance.
- Reduce the Record Quantity
- Avoid Correlated Subqueries
- Consider a Materialized View
- Add Directives to the Planner
Reduce the Record Quantity
A slow query which returns a few records may actually be processing many records in the early stages of the query, with the more restrictive filters (to reduce the result set) applied at the end of the query processing.
In this case, you can use a Common Table Expression (CTE) to apply the restrictive filter first, then execute the query on the CTE table.
In these examples, the query is used to obtain the first last_name in each zip_code.
Here is the standard query, with a 7 second execution time:
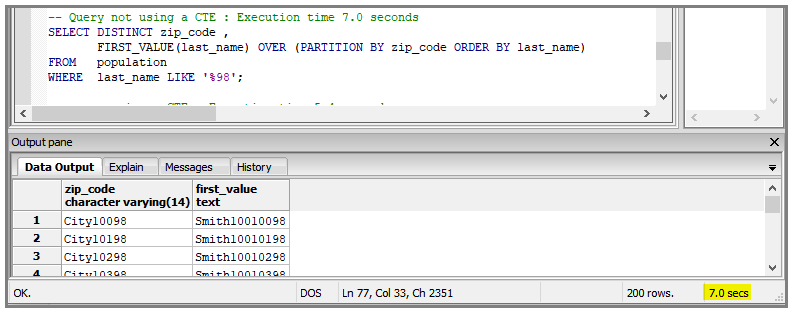
Here is the refactored query using a CTE to reduce the number of records. The execution time is 5.4 seconds.
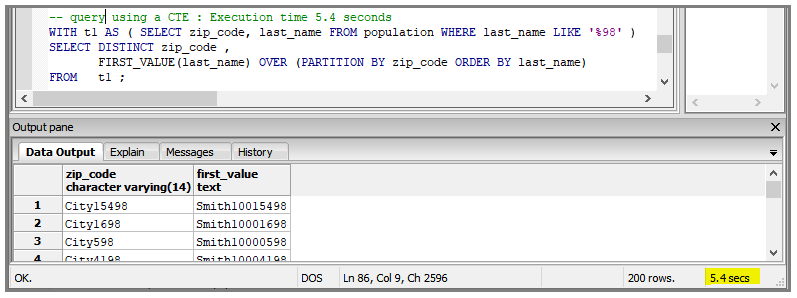
Avoid Correlated Subqueries
A correlated subquery is a subquery that refers to columns of the outer query. The problem with correlated subqueries is the high number of times it must be executed: once for each row processed by the outer query. Avoid correlated subqueries whenever possible.
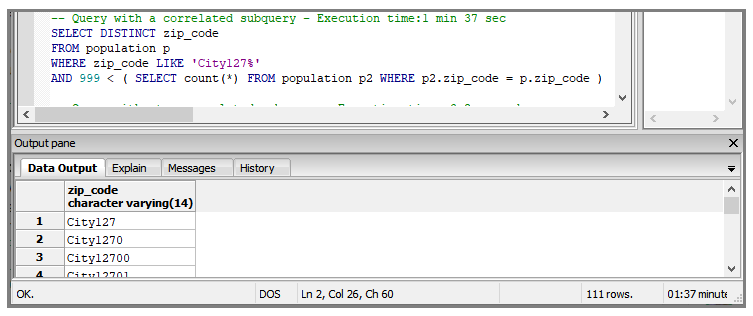
This example uses a correlated subquery to obtain the zip_code for cities with a population of 1000 or above. The execution time is 1 minute 37 seconds
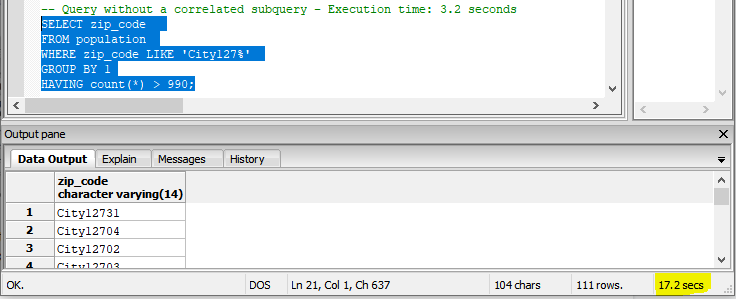
Here is the refactored query without using the correlated subquery. The execution time is 17.2 seconds.
Consider a Materialized View
SQL views obtain the view records online using in the FROM clause. The online calculation of the view records can affect the query performance. Materialized views can improve query performance in some cases. There are considerations with using materialized views. For example, the view must be refreshed frequently for accurate results.
For this region population example, data refreshed daily is highly accurate.
This view groups any zip_code that starts with the same 3 digits and obtains the population in the region:
CREATE VIEW region_population AS
SELECT substring(zip_code, 1, 7) AS region, count(*) AS pop
FROM population
GROUP BY substring(zip_code, 1,7)
This is the query to obtain the population for the regions in the range City200 to City250:
SELECT region, pop
FROM region_population
WHERE region BETWEEN ‘City200’ AND ‘Citi250’
When the query is executed, the view region_population records are calculated as part of the query, adding extra time to the query execution time.
If you create a materialized view, the view records are not calculated each time the query is run. This example creates the materialized view:
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW region_population AS
SELECT substring(zip_code, 1, 7) AS region, count(*) AS pop
FROM population
GROUP BY substring(zip_code, 1,7)
Execute the query:
SELECT region, pop
FROM region_population
WHERE region BETWEEN ‘City200’ AND ‘Citi250’
The query is faster without having to calculate the view records.
Add Directives to the Planner
This is a non-standard technique offered by only a few SQL database engines.
Some database engines support adding execution directives in the query. For example, you can specify an index to use, or an index to not use, and what table to read first.
For example, this Oracle query includes a directive for which index to use:
SELECT /*+ INDEX (employees emp_department_ix)*/ employee_id, department_id
FROM employees
WHERE department_id > 50;
The optimizer directive is included as a comment, enclosed with /* */ to specify the index emp_department_ix of the table employees.
Closing Words
In this lesson you learned about indexes, functional indexes, and techniques to refactor your queries to take advantage of indexes. Keep going, learn SQL and increase your skills!
IN THIS PAGE





